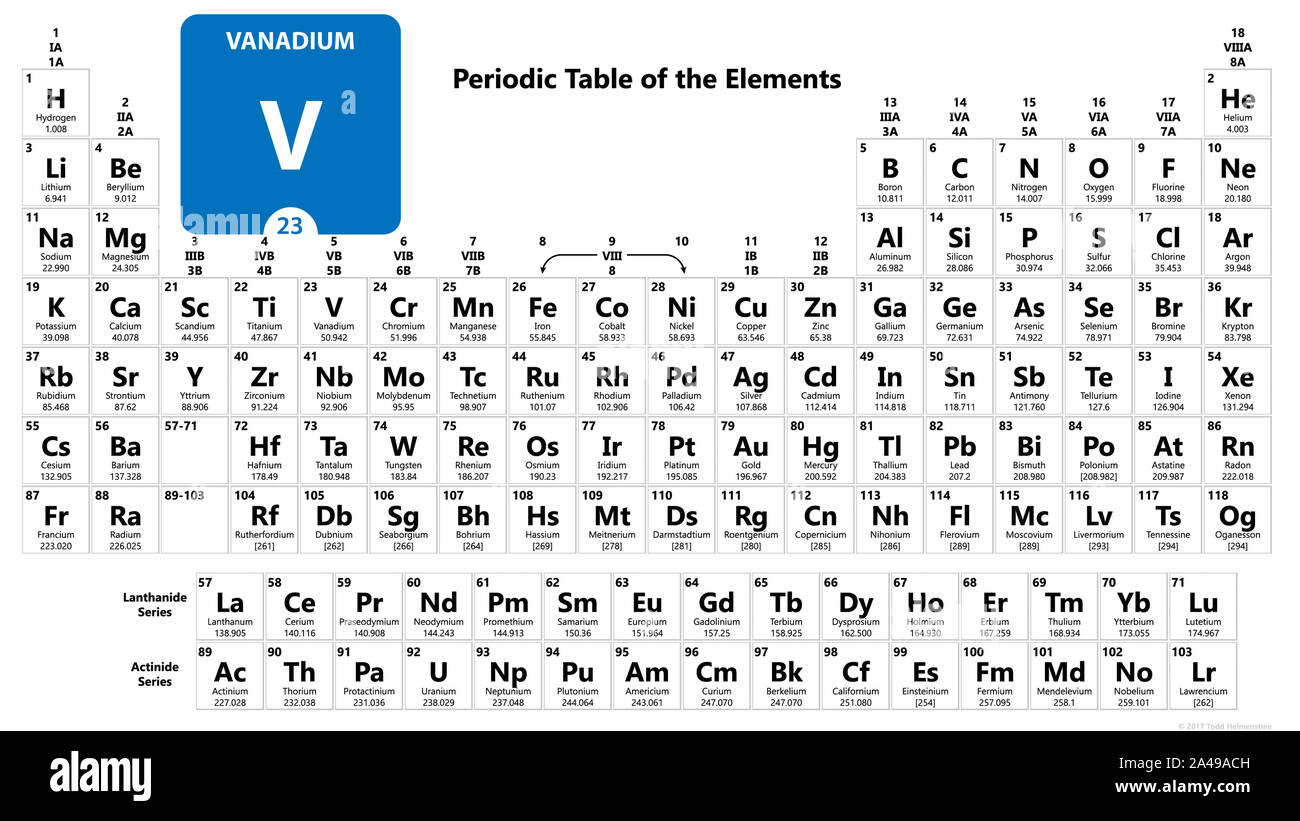
Atomic Number of Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with atomic number 23 which means there are 23 protons and 23 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Vanadium is V. Atomic Mass of Vanadium. Name: Vanadium Symbol: V Atomic Number: 23 Atomic Mass: 50.9415 amu Melting Point: 1890.0 °C (2163.15 K, 3434.0 °F) Boiling Point: 3380.0 °C (3653.15 K, 6116.0 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 23 Number of Neutrons: 28 Classification: Transition Metal Crystal Structure: Cubic Density @ 293 K: 5.8 g/cm 3 Color: Silverish Atomic Structure. Atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus): 23 Atomic symbol (on the periodic table of the elements ): V Atomic weight (average mass of the atom): 50.9415. Vanadium (V) is a bright white soft metal that has the atomic number 23 in the periodic table. It is a Transition metal and located in Group 5 of the periodic table. It has the symbol V. The atomic number of vanadium is 23, and atomic mass is 50.914 g/mol. Vanadium melts at 1910oC and boils at 3407oC.
Vanadium is a metallic element with the atomic number 23 and the symbol V. On the periodic table of elements, it is found in Group 5, and in Period 4 between titanium and chromium. It is referred to as a “transition metal.”
Vanadium is a soft, ductile element. Described as silvery-white in color, or, when it is a powder, as light-gray with a silvery sheen.
Although vanadium’s discovery is often credited to Swedish chemist Nils Gabriel Sefström, but in fact the discoverer was Spanish professor of mineralogy Andrés Del Rio, who in 1801 found the element in Mexico and named it erythronium. Persuaded that it was nothing new, Del Rio dropped his claim, and Sefstrom receives credit. It was German chemist Friedrich Wöhler who proved in 1831 that the discoveries were identical.
Vanadium is named for the Norse goddess who also goes by the name Freyja, who is a member of the group of deities called Vanir. She is the goddess of death and love, marriage, and fertility.
Atomic Number Of Vanadium 51
Always found combined with other elements in minerals, coal, and petroleum, vanadium is used both in an alloyed and unalloyed states. It is mined in the United States in Arizona, Utah, and Colorado, as well as in Africa, Peru, and Venezuela. About 7,000 tons per year are produced.
Vanadium has a number of uses. It is used to increase the strength and toughness of steel, primarily in the creation of the iron alloy ferrovanadium. The steel is used in jet engines, for example. In compounds V205 and NH4VO3, which are oxidation catalysts, vanadium finds uses in the chemical industry. Vanadium pentoxide is also used as a dye and color fixer.
Recent studies explore whether vanadium might have a role in helping to lower the blood sugar levels of people who have diabetes. Other studies have hinted that vanadium may have a role in the formation of the skeleton in animals. Between 10 and 60 mcg of vanadium is consumed daily in a normal diet.
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| 50V | 49.947 156(3) | 0.002 50(10) |
| 51V | 50.943 957(3) | 0.997 50(10) |
In its 1961 report, the Commission accepted Ar(V) = 50.942 based on mass-spectrometric data, and in 1969 recommended a more preciseAr(V) = 50.9414(3). A number of determinations of the isotopic composition of vanadium have since been considered.As a result, in 1977 the Commission refined Ar(V) to 50.9415(1). The isotopic composition of vanadium from five chondritic meteorites has been shown identical within experimentalerror to the terrestrial diabase W-1 and a laboratory standard.
Two stable isobars, 50Ti and 50Cr, are the immediate neighbours in the chart of nuclides, to 50V,whose β+ and β- decay modes are, therefore, predictable. The nuclear angular momentum of 50V, however,is high but consistent with long half-lives, evidently too long to be readily observed. The isobarsrender the mass-spectrometric determination of the abundance of the isotope 50V subject to carefulchemical determination of the trace presence of Ti and Cr.
© IUPAC 2003
The Atomic Number Of Vanadium Chromium Manganese

Atomic Number Of Molybdenum
CIAAW
Vanadium Element Protons Neutrons Electrons

Vanadium Atomic Structure
Vanadium
Ar(V) = 50.9415(1) since 1977
The name derives from the Scandinavian goddess of love and beauty, Freyja Vanadis, because of itsmany beautiful multi-coloured compounds. Vanadium was discovered by the Swedish physician and chemist Nils-Gabriel Sefström in 1830.
Vanadium had originally been discovered by the Spanish mineralogist Andres Manueldel Rio y Fernandez in 1801, who named it erythronium, after the plant of that name whose flowershave many beautiful colours. Del Rio later decided that it was really chromium in his lead sample.Vanadium metal was first isolated by the English chemist Henry Enfield Roscoe in 1869.
